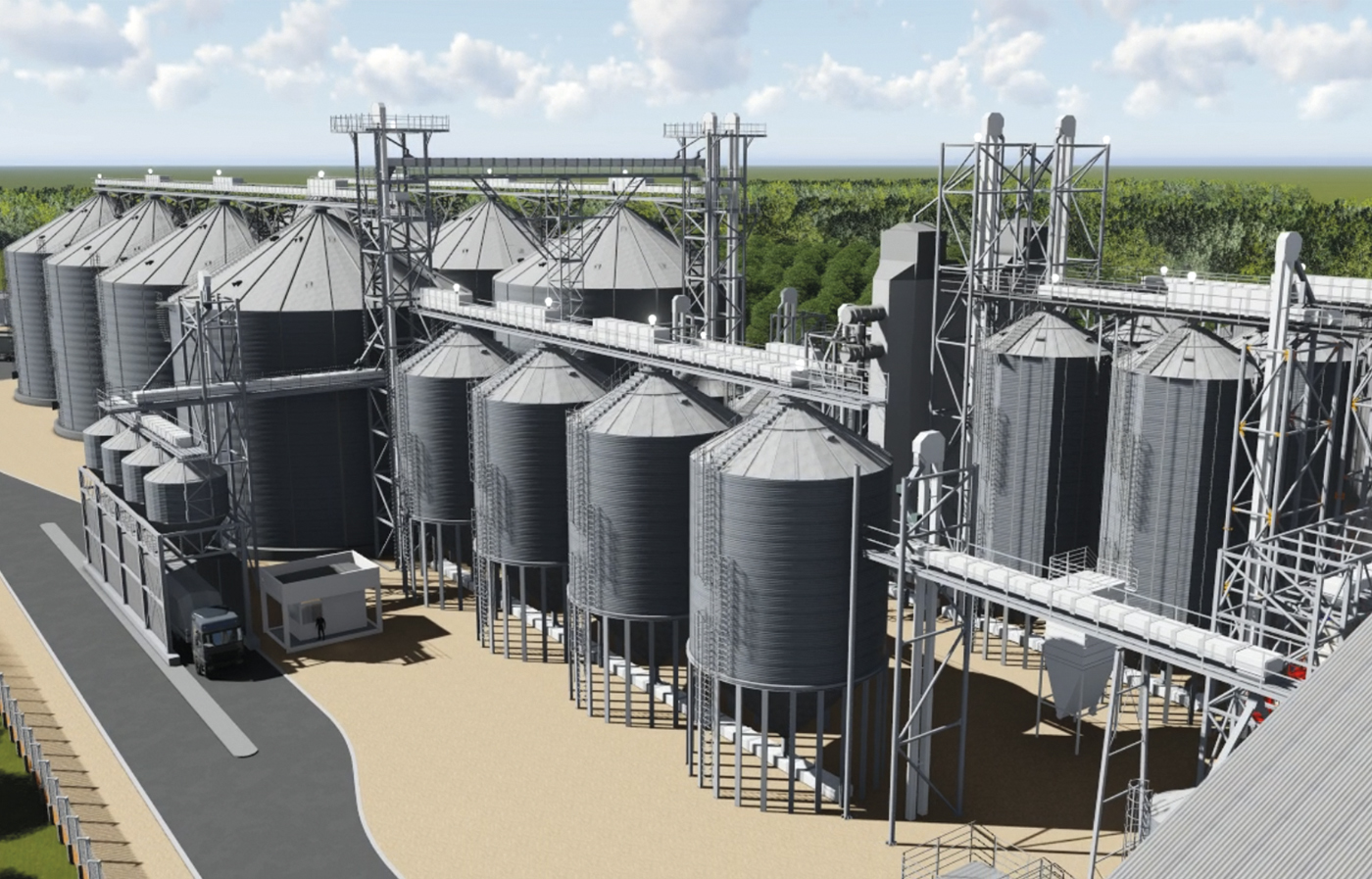
At Silos Córdoba, experts in the manufacturing of metal silos for grain storage, we understand that designing a silo plant requires considering several key aspects. This approach ensures optimized grain management and guarantees sustainability.
Below, we highlight the essential points:
Key Aspects for an Efficient Silo Plant
♦ Efficiency and functionality: First, it is essential to design a continuous and agile flow that optimizes time and resources in grain handling.
♦ Flexibility: Additionally, the plant must be adaptable to handle different types of grain according to changing market demands.
♦ Space for expansion: Moreover, planning for future extensions without disrupting current operations ensures scalability.
♦ Automation: Incorporating advanced technologies, such as grain drying systems, temperature monitoring, and humidity control, also enhances efficiency.
♦ Low operating costs: For example, designing systems that optimize energy consumption, maintenance, and staffing can generate significant long-term savings.
♦ Sustainability: Finally, reducing emissions and efficiently utilizing natural resources like water and energy is vital to minimizing environmental impact.
Fundamental Stages in Silo Plant Design
1.Reception: This stage includes unloading grain into reception pits, ensuring a continuous flow to subsequent phases.
2.Conditioning: Here, processes such as pre-cleaning, cleaning, drying, and sometimes cooling are carried out. This ensures clean, high-quality grain before storage.
3.Storage: In this stage, grain is conserved in metal silos equipped with ventilation and thermometry systems to maintain its quality.
4.Dispatch: Lastly, grain is transported from silos to trucks, trains, or packaging systems, ensuring precision and efficiency throughout the process.
Silo Plant Design: Essential Stages
Here is the design of a grain storage plant, which includes the following fundamental stages:
– Reception: Features a reception pit connected to bucket elevators, ensuring efficient grain transport to the next phases of the process.
– Conditioning: Includes areas for pre-cleaning, cleaning, and drying, complemented by buffer silos to handle high volumes and cooling silos to stabilize grain temperature after drying.
– Storage: Comprises storage silos equipped with ventilation and thermometry systems, connected to elevators to preserve grain quality and facilitate handling.
– Dispatch: Equipped with silos for direct loading onto trucks or trains, with weighing systems and sampling stations to ensure precision in deliveries.
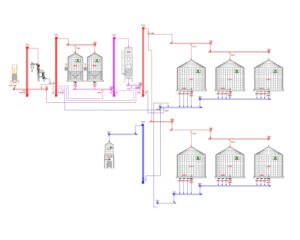
An Efficient and Modular Design
This design allows for handling large grain volumes with efficient control at every stage, optimizing product quality and safety. Moreover, to ensure robust and adaptable operations, the following can be integrated:
– Additional transport systems: For instance, these minimize risks in case of failures or interruptions.
– Advanced monitoring: Sensors for humidity, temperature, and CO₂ with centralized control simplify monitoring.
– Cleaning and sorting equipment: Advanced options ensure superior grain quality.
– Subproduct management systems: Finally, solutions for collecting and reusing residues improve the plant’s sustainability.
By implementing these enhancements, the design will become more versatile and better prepared to meet current and future industry demands.
At Silos Córdoba, with over 45 years of experience and projects in more than 45 countries, we offer turnkey solutions for grain storage plants. Our commitment is to design facilities that are efficient, modular, and sustainable, tailored to the specific needs of each client.

